Cannabigerol (CBG) is often overshadowed by its more famous cannabis-derived counterparts, CBD and THC. However, as the "mother of all cannabinoids," CBG holds a pivotal role in the biochemistry of cannabis plants and potentially in wellness and medical treatments. This guide delves into the science of CBG, exploring its mechanisms, benefits, and what enthusiasts and consumers need to understand about this lesser-known compound.
[These statements are not medical advice and have not been evaluated by the FDA]
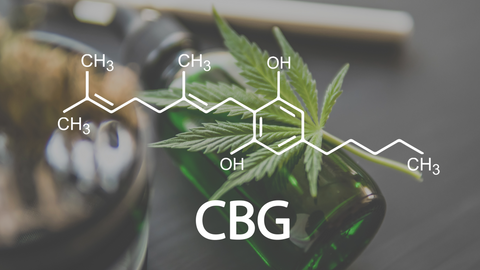
What is CBG?
CBG is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in cannabis plants. Typically present in low concentrations, it's the chemical parent to THC and CBD, among other cannabinoids. Through the plant's development, CBG is converted to THC, CBD, and other cannabinoids through natural enzymatic processes. Due to its pivotal role, CBG is crucial for the biosynthesis of cannabis compounds, meriting the title "stem cell" of cannabinoids.
How Does CBG Work?
Like CBD, CBG interacts with the body's endocannabinoid system (ECS), but it does so in a unique manner. The ECS is responsible for maintaining homeostasis within the body, regulating functions such as mood, appetite, pain response, and immune system reactions. CBG binds to both CB1 and CB2 receptors in the ECS, possibly influencing mood, pain management, and inflammation.
CBG's interaction with the ECS suggests it could have various therapeutic benefits. Unlike THC, it doesn't produce a high, making it a subject of interest for its potential medical applications without psychoactive effects.
Potential Benefits of CBG
Research on CBG is in its early stages, but preliminary studies suggest several potential health benefits:
- Neuroprotective Properties: Studies indicate CBG might protect neurons in neurodegenerative diseases like Huntington's disease.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: CBG has shown promise in reducing inflammation, particularly in models of inflammatory bowel disease.
- Cancer-Fighting Potential: Early research suggests CBG might block receptors that cause cancer cell growth.
- Antibacterial Properties: CBG has been observed to act as an antibacterial agent, particularly against MRSA microbial strains resistant to several classes of drugs.
- Appetite Stimulation: CBG could help stimulate appetite, offering potential support for conditions like cachexia and eating disorders.
CBG is available in various forms, including oils, tinctures, gummies, and topical applications. The choice depends on personal preferences, desired effects, and specific health concerns. As with any cannabinoid product, starting with a low dose and gradually increasing it to gauge the body's response is advisable.
What to Know Before Using CBG
- Legality: The legality of CBG products can vary by location, depending on cannabis laws.
- Quality Control: Look for third-party tested products to ensure purity and potency.
- Consult Healthcare Providers: Before adding CBG to your regimen, especially if you have existing health conditions or take medication.
CBG's potential goes beyond being a precursor to other cannabinoids. Its unique interaction with the ECS and promising benefits for various health conditions make it a cannabinoid worth watching. As research evolves, we may discover more about CBG's role in wellness and therapy. For those curious about incorporating cannabinoids into their health routine, CBG offers an intriguing, non-psychoactive option to explore.



Comments (0)
There are no comments for this article. Be the first one to leave a message!